Google Pay (now Google Wallet) is Google’s own digital wallet app. It’s one of the most popular digital wallet/payment apps on the market, with 150 million users worldwide.
Google Pay owes its popularity to its ease of use. Users can store multiple different payment cards and other documents in Google Wallet, effectively allowing them to ditch their physical wallet altogether.
But many existing and potential Google Pay users ask themselves the same question – Is Google pay safe?
After all, how safe can it be when you can complete payments with little more than a tap on your phone screen?
Well, rest assured, Google has put a lot of thought into making its payment app as secure as possible. This includes measures to stop deliberate fraud, and precautions to stop accidental misuse.
In this guide we’ll look at the various security features that Google has built into its payment app, and explain what else you can do to fight payment fraud and card misuse.
What is Google Pay and how does it work?

Before we look at security features, we need to explain how Google Pay works.
There’s a bit of confusion surrounding Google Pay and Google Wallet. Google recently merged Google Pay into Google Wallet, meaning that you now get the functionality of both apps in one.
Where Google Wallet was the app that you use to store your cards, IDs, tickets, and all sorts of other documents, Google Pay was specifically for making payments using the cards stored in Google Wallet.
Now the functionality of both apps (storage and payment) have been rolled into one as Google Wallet. But, this is a relatively new change, and most people still refer to Google Pay when making digital payments.
Google Wallet isn’t just available on Android devices. You can use it on tablet, PC, smartwatch, and even download it for free on iOS.
This means you can use Google Wallet for payment online and in-store. For online payments, simply tap the Google Pay button at checkout, choose which card you want to pay with, and complete your order.
The Google Pay button can appear in a few different ways, some of which you can see below.

For in-store payments, Google Pay uses your phone’s built-in NFC chip to replicate a contactless card payment. While older phones don’t have this functionality, almost all new phones do, and it’s been an industry standard for a while. You’ll just need an up-to-date version of Android or iOS and you’re good to go.
Alternatively, check out our guide to find out how to add your cards to Apple Wallet.
What security features does Google Pay have?

Now let’s move onto the security features that Google Pay and Google Wallet use to keep your money safe.
Tokenized card details
Like all other digital wallet and digital payment apps, Google Pay stores your payment card details digitally on your device. This includes the standard information needed to complete a transaction, i.e. your card number, your security code, and your sort code.
But what happens if someone manages to gain access to your phone? Or manages to intercept your payment details while you’re completing a transaction?
Google Wallet uses a technique called tokenization to protect your card details. Rather than storing your actual card number and other info, Google stores your details as a random string of numbers called a virtual account number.
This virtual account number has no value on its own, it has to be matched to the encrypted data on Google’s servers to complete a transaction. In this sense, tokenization is much safer than encryption in digital payment applications because there’s no way to link the token back to your actual card details.
Screen lock
To use Google Wallet, either via the app or via your lock screen, you have to submit some form of passcode. This can be any one of the following, which we’ve listed in order from least to most secure:
- Pattern
- PIN
- Password
- Fingerprint
- Iris scan
- 3D face scan
This means that, even if someone manages to steal your phone, they can’t complete a payment unless they have access to your passcode. Biometric identification is the most secure, which is why it’s recommended as the best way to unlock your phone.
As an additional precaution, you can only use Google Pay if you have a screen lock enabled on your phone. If your screen lock is removed Google will automatically wipe your card details from Google Wallet.
Verification for new cards
Another important security measure employed by Google Wallet is verification for new cards. Whenever you add a new card, you’re required to confirm your identity. This helps protect your cards and stops people from being able to add stolen cards to another Google Wallet account.
The verification process happens via your bank. There are a few different ways to verify a new card:
- Via email or text
Your bank will send a code via SMS which you have to enter in Google Wallet to complete the verification process.
- By phone
Your bank will provide you with a verification code via phone call.
- Via your bank’s app or website
You can sign in to your bank’s app or website to complete your verification.
- By temporary deposit
Google will send you a 6-digit confirmation code in a temporary charge that will appear on your bank statement.
Google Wallet may ask you to complete verification at other times too, including:
- To verify certain transactions
- To access certain content
- If Google detects suspicious activity on your account
- To provide additional information for regulatory purposes
While this verification process does add a bit more friction to the user experience, it’s a security measure that helps keep your money and data safe.

Google’s secure servers
Alongside on-device security measures, Google protects your data with a range of server security protocols, including encryption in transit and encryption at rest.
Encryption in transit secures your data after a connection with Google servers has been established and authenticated, i.e. as it makes its way to and from your device. This stops attackers from intercepting your data.
Encryption at rest, on the other hand, protects your data as it’s stored on Google’s servers. Google’s server locations are also heavily monitored and can only be accessed by a small handful of Google employees with security clearance.
You can read more about these features in Google’s Google Pay Security Paper.
Google Pay security compliance
All of the security measures and protocols we’ve mentioned above play an essential role in making Google Pay/Google Wallet compliant with industry security standards. The two most important industry security requirements are Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and Secure Customer Authentication (SCA).
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
PCI DSS is a set of 12 requirements which ensures that all companies that process, store or transmit payment card information maintain a secure data environment:
- Use and maintain firewalls
- Do not use vendor supplied default passwords
- Protect stored cardholder data
- Encrypt transmission of cardholder data across open, public networks
- Protect all systems with regularly updated antivirus software or programs
- Develop and maintain secure systems and applications
- Restrict access to cardholder data within the business in question on a strict ‘need to know’ basis
- Use unique IDs for all employees with access to customer data
- Restrict physical access to cardholder data
- Track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data
- Regularly test security systems and processes
- Maintain a policy that addresses information security for all personnel
You can find out more about Google’s PCI DSS compliance here.
Secure Customer Authentication (SCA)
Secure Customer Authentication is a security requirement that is in place across the EEA (European Economic Area) and in the UK. It’s part of the EU’s Second Payment Services Directive (PSD2) which aims to protect electronic payments using multi-factor authentication.
PSD2’s primary focus is tackling card-not-present fraud, which happens when fraudsters use stolen card details. SCA helps prevent this by requiring two of the following authentication factors when customers carry out electronic payments:
- Something that the cardholder “knows”, e.g. a password or a PIN
- Something that the cardholder “has”, e.g. a one-time passcode on a personal device like a smartphone
- Something that the cardholder “is”, e.g. biometric verification via fingerprint or facial identification
This is why Google Wallet requires additional verification for new cards, as we mentioned earlier.
Potential risks and how to combat them

Google Pay has multiple layers of security and adheres to various protocols to help keep your money safe. But, as with every payment method, there are a couple of risks that you should be aware of.
Ultimately, Google Wallet is only as secure as your password. If someone does manage to obtain your phone passcode, they can theoretically use your digitally stored cards and use them to make payments.
As a result, it’s highly recommended that you secure your phone using biometric identification. If you do choose to use a PIN or password, you should make them as secure as possible — the longer the better. Pattern locks are by far the least secure way to lock your phone, so avoid them if you use a digital wallet, or any other sensitive application on your phone.
Virtual cards are an even more secure version of the digital cards that you can store in Google Wallet. Virtual cards use a randomly generated card number to make virtual card payments, and can be issued with custom spend limits and expiry dates as an added security measure.
Finally, it’s important to note that Google Pay doesn’t offer buyer protection. However, in most cases this shouldn’t be an issue. Google Pay is an intermediary service, and you’ll be covered by your payment card’s buyer protection if you use it via Google Pay. In this sense it’s important to note whether you’re using a credit card or a debit card because each comes with different levels of buyer protection.
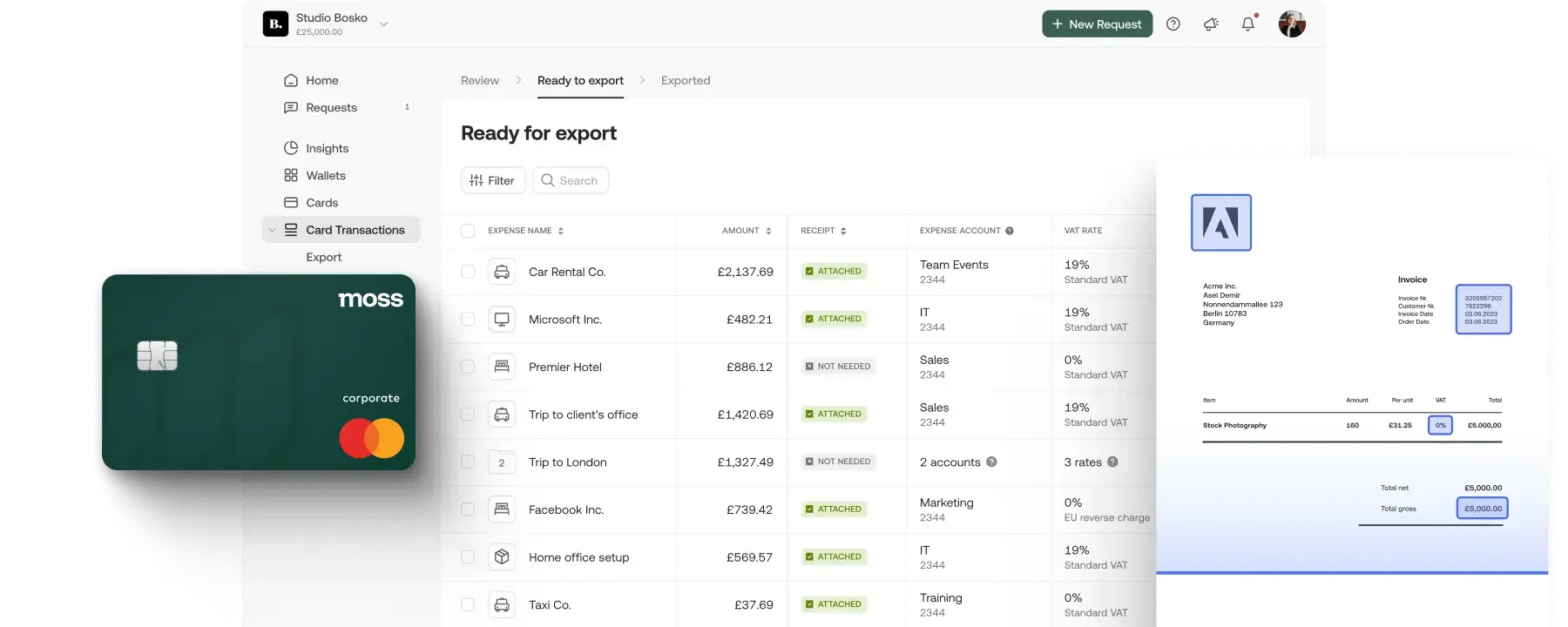
Using Moss corporate cards with Google Wallet

As we’ve explained, Google Wallet/Google Pay is currently one of the most secure ways to make payments both online and in-store. It has many different security features which make it safer than both cash and card payments.
The good news is that you can take advantage of Google Wallet’s industry-leading security when making business payments with Moss. Moss corporate credit cards give your business access to £2.5 million credit each month. You can allocate and track custom budgets for each and every employee in your organisation, and freeze cards whenever you need via the Moss app.
This gives your employees access to company funds for travel expenses and more, while allowing you to maintain crucial control over spend. This can save you and your team huge amounts of time and money in the long run, and increases all-round accountability. You can add your Moss card to Google Wallet in just two minutes, and be ready to spend directly from your smartphone with just a few taps.
FAQs
Google Wallet and Google Pay used to be separate apps — one for storing payment cards and IDs, and one for completing electronic payments. But Google recently rolled Google Pay into Google Wallet, so you can access both of these functionalities from the same app.
Google Pay is PCI DSS compliant. Google meets all PCI DSS criteria to ensure that your card and payment information is secure when making electronic payments.
Google Pay is also SCA compliant. It requires two forms of authentication when you make payments online and in-store using your phone, laptop, or other eligible device.
Google Pay/Google Wallet is available to download and use for free on iPhone, as well as via Google Chrome and Firefox on Mac.
While Google Wallet does allow you to store your payment cards on your smartphone, your cards details are stored as tokens. This means that, even if your phone is hacked, the attackers won’t be able to see or obtain your actual card details.